Abstract: According to the manufacturing process of deformation-strengthened non-quenched and tempered steel bolts, the deformation strengthening effects of MFT8 non-quenched and tempered steel raw materials, cold drawing and aging treatment were studied, and their deformation hardening index and mechanical properties were compared. The study analyzed the impact of the organization on its performance. The experimental results show that the deformation strengthening effect of MFT8 non-quenched and tempered steel is obvious; after aging treatment, it still has good deformation strengthening ability, which can ensure the safety of bolts in use; the mechanical properties of bolts after strengthening meet the technical requirements of 8.8. Research materials can replace high-strength bolts made of quenched and tempered steel.
Standard bolts are used in large quantities and in a wide range of engineering and mechanical fields. Deformation-strengthened non-tempered steels can be used to manufacture 8.8 high-strength bolts, eliminating the need for quenching and tempering processes, reducing heat treatment processes and equipment, reducing energy consumption, and shortening production cycles. It avoids the waste caused by deformation or quenching crack in the heat treatment process and has broad application prospects.
The deformation hardening index n is usually used to indicate the deformation strengthening ability of the material. The larger the n value, the larger the uniform deformation amount, the better the cold forming performance and the stronger the strengthening effect. The main production process of non-quenched and tempered steel bolts is: hot-rolled wire rod-pickling-cold-rolling-rolling-aging, the deformation of the raw material after cold drawing, its mechanical properties, whether it can replace the quenched and tempered steel to manufacture high-strength bolts, Whether the margin of deformation strengthening after aging can ensure the safety of bolt use requires experimental research.
1 Experimental materials and methods
The raw material of MFT8 steel is φ9mm hot-rolled wire, and the chemical composition (% by mass) is: C0.21, Si 0.13, Mn1.37, P 0.015, S 0.005, Nb0.04, Al 0.047. The experimental materials were cold-drawn and strengthened after pickling and surface pretreatment, and the reduction ratios were 25% and 30%, respectively.
Tensile tests were carried out on raw materials, cold drawn materials and aging samples on an electronic universal testing machine, and the strain hardening index was calculated at random points in the uniform deformation interval, and 5 times samples were selected according to GB/T 228-2002 standard. The morphology of the tissue was observed on a scanning electron microscope. Longitudinal wire cutting was used to prepare a transmission electron microscope sample, and the microstructure was analyzed by transmission electron microscopy after double-spray electrolysis thinning.
The experimental scheme is as follows: (1) research on the deformation strengthening effect of raw materials, judging the cold forming properties and the effect of deformation strengthening; (2) comparing the deformation strengthening effects of two cold drawing materials with different reducing ratios, and preferably one of them is subjected to aging treatment; (3) Analyze whether the final mechanical properties of the bolt product meet the technical requirements after aging, test the final deformation strengthening index, and predict the reliability of its use.
2 Experimental results
2.1.1 Material deformation strengthening effect and performance under various conditions
8.8 grade (M no more than 16mm) bolt technical requirements: tensile strength greater than 800MPa; yield strength greater than 640MPa; elongation after fracture is 12%; HRC 23~32. The tensile test was used to test the n value and performance of raw materials and cold drawn materials. After the cold drawing of the bolt, due to the effect of the Bowinger effect, the forming resistance will decrease with the increase of the cold drawing rate. At 30%, the Bauschinger effect is the largest and the compressive true stress is the smallest. The bar with a rate of 30% was subjected to 300 ° C, 2 h aging treatment, and the n value and performance index were tested. The performances are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 Mechanical properties of MFT8 steel
Table.1 Mechanical properties of MFT8 steel
Material status
Strain hardening index n
Tensile strength MPa
Yield strength MPa
Yield ratio
Elongation      % Â
rate of reduction in area%
Raw material
0.59
747.5
625.7
0.8371
33.5
72.5
Cold pull reduction rate 25%
0.315
945
864.6
0.91
22.5
62.5
Cold pull reduction rate of 30%
0.235
957.5
895.3
0.94
18.5
59.5
After aging
0.51
998.5
928
0.93
18
59
2 .2 organization of materials in various states
By using microalloying technology, a small amount of alloying element Nb is added to the low carbon steel, and the controlled rolling and controlled cooling causes the carbonitrides in the raw material ferrite and pearlite to be dispersed, resulting in precipitation strengthening and fine grain strengthening. The base material of the raw material is fragmented pearlite + ferrite with a grain size of 5 μm, and there are obvious precipitates in the enlarged ferrite grains, as shown in Figs.
In order to further improve the strength of the material, the raw materials were cold-deformed. After cold drawing, the metallographic structure and grain size did not change much, but a large number of dislocations were formed inside the ferrite, and dislocation entanglement formed a cellular substructure. As shown in Figure 3a. After the aging treatment, a subgrain boundary was formed in the ferrite, and the dislocation morphology changed, as shown in Fig. 3b.
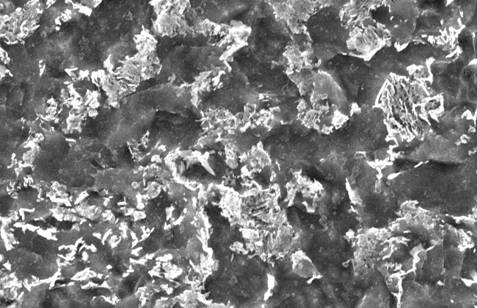
Figure 1 Ferrite + broken pearlite


Figure 2 Precipitates in ferrite grains
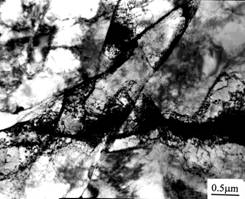
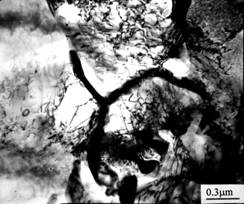
      Figure 3 Before (a) after aging treatment (b) Dislocation density in ferrite, (TEM)
3 Analysis and discussion
During the entire deformation process of the metal, after the external force exceeds the yield strength, the plastic deformation does not continuously flow like the yielding platform, and it is necessary to continuously increase the external force to continue. This indicates that the metal material has an ability to prevent further plastic deformation, which is the deformation strengthening property. The strain hardening index n reflects the ability of the metal material to resist deformation and is a performance index for characterizing the strain hardening behavior of metal materials. In the extreme case, n=1, indicating that the material is a perfectly ideal elastomer, S is proportional to e; when n=0, S=K=constant, indicating that the material has no strain hardening ability, such as recrystallization at room temperature. Soft metal and materials that have been strongly strain hardened.
The experimental results show that the raw material has a high n value and good cold deformation ability. The reduction ratio is increased from 25% to 30%. With the increase of plastic deformation, the strengthening effect increases, and the mechanical properties of all the bolts meet the technical requirements of 8.8 bolts. Plastic deformation is the cause of strengthening, and strengthening is the result of plastic deformation. As the amount of deformation increases, the value of n decreases, and the ability of the material to continue to strengthen is weakened. The deformed material with a 30% reduction ratio has an n value of 0.235, which indicates that it still has a certain ability to resist overload failure. The tensile fractures of the above three states all show that the material is ductile fracture, which indicates that the strength of the material after deformation is improved, but it still maintains a tough state.
The type and nature of the lattice of the metal determine its deformation strengthening effect [7]. The slippage of the metal, the difficulty of forming the cell structure, and whether the slip of the screw dislocation can proceed smoothly and other factors have a significant effect on the value of n. The following characteristics of the raw materials make it have a very high deformation strengthening ability: fine grains; easy to cross-slip ferrite structure; effect of interstitial carbon on deformation strengthening; carbonized material points formed by Nb in the material, In the process of plastic deformation, the combination of various factors makes the experimental material have a good deformation strengthening potential, so the test results show a higher value of n.
As shown in Fig. 4, after cold drawing, a large number of dislocations are formed inside the ferrite, and dislocation entanglement forms a cellular substructure, and the n value decreases as compared with the raw material, and the residual plasticity decreases.
The non-quenched and tempered steel bolts used in the cold-worked state have high density of movable dislocations and other defects in the deformed structure, making them unstable. When the bolts are loaded, these movable dislocations will climb, causing a slight yield and affecting their performance. The aging treatment stabilizes the movable dislocations and also enables the non-tempered bolts to have good overall performance. Due to the aging treatment of the blade dislocation, sufficient energy can be obtained to make the climb, so that the irregular dislocations on the slip surface are redistributed and arranged into a wall to form a sub-crystal. Therefore, the n value is restored after the aging, and the plasticity is basically maintained. The higher residual n value guarantees the ability of the bolt to resist accidental overload during use.
4 Conclusion
(1) MFT8 non-tempered steel has good deformation strengthening potential and is suitable for cold work strengthening;
(2) After the deformation strengthening, the mechanical properties of the experimental materials reach the technical requirements of 8.8 bolts, which can replace the quenched and tempered steel.
(3) After the aging treatment, the value of n is restored and the safety of the bolt is ensured.
Related links: MFT8 material query ( click on the image below to enter the material query URL )
Kitchen faucet is a necessary product in our kitchen. Different type can make your life more convenience.
Kitchen faucet can be made of different materials, such as copper and stainless steel. Brass kitchen faucets are mostly made of lead free brass, or DR brass or Hpb59-1. Some low end products are made of recycle brass, which would have more impurities. The stainless steel kitchen faucets are becoming more popular with the improvement of the production process.
Kitchen faucets are available in a variety of colors. Electrical chrome plated is still the most popular one though more and more colorful finished faucets are supplied in the market. The production process can be PVD, electrical plated, powder coated, ORB etc. Color options have black, matt black, white, matt white, nickel brushed, gold, rose gold, gun mental etc.
Kitchen Faucet,Kitchen Taps,Modern Kitchen Faucets,Kitchen Water Tap
Kecheng Trading Company Limited , https://www.jmttl.com
