After installation of the PV system, the user is most concerned about the amount of power generated, because it is directly related to the user's return on investment. There are many factors that affect power generation, such as components, inverters, cable quality, installation orientation, azimuth, tilt angle, dust and shadow shielding, component and inverter ratio system solutions, line design, construction, grid voltage, and so on. Factors are possible. This series of articles will discuss various factors based on actual cases. This article focuses on the impact of component factors on the system.
First, the impact of component dust
For long-term operation of photovoltaic power generation systems, dust from the panel must not be underestimated. The dust on the surface of the panel reflects, scatters, and absorbs solar radiation, which reduces the solar transmittance, reduces the amount of solar radiation received by the panel, and reduces the output power. The effect is directly proportional to the cumulative thickness of the dust.
1, the temperature effect
At present, photovoltaic power plants mostly use silicon-based solar cell modules, which are very sensitive to temperature. As the dust accumulates on the surface of the modules, the thermal resistance of the photovoltaic modules increases, becoming a thermal insulation layer on the photovoltaic modules, and affecting the heat dissipation thereof. . After the component is blocked, the bypass protection element in the junction box behind it will be induced to start. A DC current of about 9 A in the assembly string will be instantaneously loaded on the bypass device, and the junction box will generate more than 100 degrees of high temperature. High temperature has little effect on the battery panel and the junction box in the short term, but if the shadow effect is not eliminated and persists for a long time, it will seriously affect the service life of the junction box and the battery panel. In industry news reports, the junction box is often burned and blocking is one of the culprits.
The current and voltage of some battery monoliths in solar cell modules have changed. As a result, the product of the local current and the voltage of the solar cell module increases, and a local temperature rise occurs in these battery modules. The defects of certain battery cells in the solar cell module may also cause the device to generate heat locally during operation. This phenomenon is called “hot spot effectâ€. When the hot plate effect reaches a certain level, the solder joint on the component melts and destroys the gate line, resulting in the rejection of the entire solar cell module. According to industry data, the hot spot effect reduces the actual life of solar modules by at least 10%.
2, occlusion effect
Dust adheres to the surface of the panel and blocks light, absorbs and reflects light.
The most important of these is the shielding effect of light, which affects the absorption of light by the photovoltaic panel, thereby affecting the photovoltaic power generation efficiency. Dust is deposited on the light receiving surface of the panel assembly. First, the surface of the panel is reduced in light transmittance; second, the incident angle of some of the light is changed, resulting in non-uniform propagation of light in the cover glass. Studies have shown that, under the same conditions, the output power of a clean panel assembly is at least 5% higher than that of an ash assembly, and the higher the amount of accumulated ash, the greater the output performance degradation of the module.
3, the impact of corrosion
Photovoltaic panels are mostly made of glass. When wet acidic or alkaline dust adheres to the surface of the glass cover, the glass surface will be slowly eroded, forming pits on the surface, resulting in diffuse reflection of light on the surface of the cover. The uniformity of propagation in the glass is destroyed. The rougher the PV module cover is, the smaller the energy of the refracted light is, and the energy actually reaching the surface of the photovoltaic cell is reduced, resulting in a decrease in the power generation of the photovoltaic cell. And a rough, sticky surface with adhesive residue is more likely to accumulate dust than a smoother surface. Dust itself also absorbs dust. Once the initial dust is present, more dust accumulates, accelerating the attenuation of the electricity generated by the photovoltaic cells.
Second, the component attenuation
The PID effect (Potential Induced Degradation) is collectively referred to as potential-induced attenuation. The direct hazard of PID is that a large amount of charge accumulates on the surface of the cell, making the surface of the cell passivated. The harm of PID effect makes the power of the battery module drastically attenuate; the filling factor (FF), open circuit voltage, and short-circuit current of the battery module are reduced; the output power of the solar power station is reduced, the power generation is reduced, and the power station revenue of the solar power station is reduced.
In order to suppress the PID effect, component manufacturers have done a lot of work on materials and structures and have made certain progress; for example, anti-PID materials, anti-PID batteries, and packaging technologies are used. Some scientists have done experiments, after the decay of the battery components in the 100 °C temperature drying 100 hours after the attenuation caused by the PID disappeared. Practice has proved that the component PID phenomenon is reversible. The prevention and control of PID problems is more from the inverter side. One is to use the negative grounding method to eliminate the negative pressure of the negative pole of the component to the ground. By raising the voltage of the component, all the components can achieve a positive voltage to the ground. This can be effective. Eliminate PID phenomenon.
Third, how to detect components from the inverter side
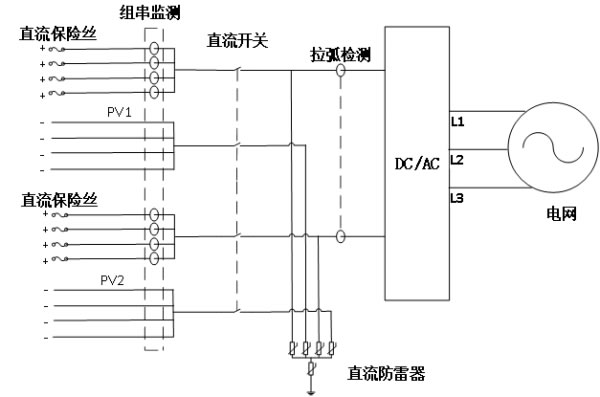
The string monitoring technology is to install the current sensor and voltage detection device at the input of the inverter component, detect the voltage and current value of each string, and determine the string operation by analyzing the voltage and current of each string. Whether the situation is obviously normal, if there is an abnormality, the alarm code is promptly displayed, and the abnormal group string is accurately located. And can upload the fault record to the monitoring system, so that the operation and maintenance personnel can find the fault in time.
Although the string monitoring technology adds a little bit of cost, it is still insignificant for the entire photovoltaic system, but it has a great effect:
(1) Early detection of component problems, component dust, splinters, component scratches, hot spots, etc., are not obvious in the earlier stage. However, by detecting the difference in current and voltage between adjacent strings, it is possible to analyze whether the string is faulty. . Deal with it in time to avoid greater losses.
(2) When the system fails, it does not require professional on-site inspection, it can quickly determine the type of fault, precisely locate which string, operation and maintenance personnel to solve in a timely manner, to minimize the loss.
The string monitoring system is as follows:
Fourth, component cleaning
Manual cleaning is the most primitive method of component cleaning and is completely based on manpower. This kind of cleaning method has low work efficiency, long cleaning cycle, high labor cost, and there are potential personal safety hazards.
Artificial dry cleaning components: Artificial dry cleaning is the use of long-staple mop with special detergents for cleaning, the use of oily electrostatic dust. The main use of electrostatic adsorption principle, with the role of adsorption of dust and sand, can enhance the ability of cleaning tools to remove dirt and dust, effectively prevent dust particles from flying during cleaning. Due to the complete reliance on manpower, there are many problems with surface remnants and unbalanced components that may cause deformation cracking. Compressed air purging blows compressed air through a dedicated device to remove dust from the surface of the module and is used in areas with scarce water resources. This method is inefficient, and there are problems with high-speed friction components of dust, and few power stations are currently used.
Artificial water washing module: artificial water washing is to spray the water on the surface of the photovoltaic module by the nozzle connected to the water wheel (or water pipe) so as to achieve the purpose of cleaning, and the pressure generally does not exceed 0.4 MPa. This type of cleaning method is better than manual dry cleaning. The cleaning efficiency is higher but the water consumption is larger. However, if the water pressure exceeds the limit, the solar cells of the photovoltaic module will be cracked, resulting in a large area short circuit, which will result in a decrease in power generation efficiency. In addition, after the water-washing assembly is naturally air-dried, water stains are formed on the surface of the components, which form shadows that block the shadows and affect power generation efficiency. The ice layer produced by the use of high-pressure water guns in winter severely weakens the optical effects of the components, especially in the northern regions.
Automatic cleaning
Semi-automatic cleaning: At present, this type of equipment is mainly converted by using engineering vehicles as the carrier. The equipment has large power and high efficiency. The cleaning work has good pressure on the components and does not cause unbalanced pressure on the components, causing cracking of the components. The cleaning can adopt two modes of sweeping and water washing. This mode is less dependent on water resources, but the requirements for the height, width, and road conditions of the array of photovoltaic modules are more stringent.
The automatic cleaning method is to install the cleaning device on the photovoltaic module array and control the rotation of the motor through the program to realize the automatic cleaning of the photovoltaic module by the device. This cleaning method is costly and the design is complicated. There are already smart sweeping robots in the country. The cleaning method is to install a sweeping robot in each PV module of the power station and clean it regularly, leaving it unattended. Photovoltaic power plants with flat terrain can be used.
Stop Valves,Cycle Stop Valves,Curb Stop Valves,Angle Stop Valves
AS-SUR INDUSTRIAL VALVE CO., LTD. , https://www.assur-valve.com
