Optimize the process conditions of trivalent chromium black passivation solution. Taking Kunshan Xiubo (KSSUPER) SL80 zinc-nickel alloy black passivation solution as the object of investigation, the factors such as passivation temperature, passivation pH, passivation time and impurity ions were sequentially investigated by single factor test. The influence of various factors on the appearance of the passivation film was investigated by an intuitive visual judgment method. The corrosion resistance of the film obtained under various conditions in 3.5% NaCl aqueous solution was studied by electrochemical potentiometric polarization curve. The appearance of the film under continuous salt spray corrosion was observed by a neutral salt spray test (NSS). The higher the temperature and the lower the pH, the faster the film formation speed. The thicker the film obtained in the same time, the better the covering ability but the poor adhesion of the film layer. At the same time, the excessive temperature will lead to the film color blooming. The passivation solution has good resistance to impurity metal ions. When the zinc ion concentration is less than 10 g/L and the iron ion concentration is less than 100 mg/L, the influence of the appearance and corrosion resistance of the obtained film layer is not changed much. The passivation film obtained under the optimum process conditions has a black and uniform appearance, and the neutral salt spray test has white rust for 240 hours, red rust for 360 hours, and excellent performance, and can be widely used in industrial production.
Key words: zinc-nickel alloy; trivalent chromium; passivation; electrochemistry; corrosion-resistant galvanized layer and zinc alloy coating are susceptible to corrosion in a humid environment, and white loose corrosion products are formed on the surface to improve the coating. Corrosion resistance usually requires passivation. At present, the more mature ones are black passivation, blue-white passivation and color passivation. Black passivation is widely used in electronic hardware, optical instruments, auto parts and other industries due to its low price and good performance. The traditional passivation process usually uses chromate passivation of hexavalent chromium, but because hexavalent chromium is relatively toxic, it pollutes the environment and is harmful to human health [1, 2], because the toxicity of trivalent chromium is only The one percent passivation mechanism of hexavalent chromium is similar to hexavalent chromium, and when combined with a suitable sealing layer, the corrosion resistance is comparable to that of hexavalent chromium, and more and more hexavalent chromium passivation processes are replaced by three prices. [3-6], it is imperative to develop a passivation solution that replaces hexavalent chromium with trivalent chromium. However, in the actual operation process, problems such as uneven color of the passivation layer or poor corrosion resistance may occur. In this paper, through a large number of single factor investigations and comparisons, the effects of process conditions and metal ions on the black passivation of trivalent chromium were studied. The optimum conditions for the passivation process were determined, and a passivation layer with excellent black light and excellent corrosion resistance was obtained.1 Experiment 1.1 Passivation process The substrate used was a low carbon cold rolled steel plate. It was ground with a No. 2000 water-sand paper to a smooth surface, and the ultrasonic waves were clearly observed in absolute ethanol and deionized water. After electroplating the alkaline zinc-nickel alloy, it was exposed to 3% dilute hydrochloric acid for 5 s, and then immersed in a passivation solution for passivation. The process flow is: degreasing → two water washing → electroplating zinc nickel → two water washing → hydrochloric acid light → two water washing → trivalent chromium passivation → two water washing → drying.
1.2 Test characterization 1) Detection of metal ions in passivation solution The metal ions in the passivation solution were determined by Beijing General Analysis TAS-990 atomic absorption spectrometer.
2) Electrochemical test The test was carried out using the CHI660 electrochemical workstation of Shanghai Chenhua Instrument Co., Ltd. The working electrode was a measuring piece of 4 cm 2 , the reference electrode was a saturated calomel electrode (SCE), the auxiliary electrode was a platinum electrode, and the corrosive medium was a 3.5% NaCl aqueous solution. The measurement was carried out at room temperature with a scan rate of 10 mv/s. Tafel data was obtained from the software analysis of the electrochemical analyzer.
3) Neutral salt spray test using the salt spray box test of Dongguan Zhongzhi Testing Instrument Co., Ltd., neutral salt spray corrosion according to GB/T 6461-2002 test standard: 5% NaCl solution for corrosive medium, pH 6.5~ 7.2, the temperature inside the spray tank is 35±2°C, the temperature of the saturated pressure tank is 47±1°C, the pressure of the gas source is 0.7~1.7kgf/cm2, and the sedimentation volume of salt water is 1-2ml/h. The sample is placed at 15° to 30° from the vertical.2 Results and discussion 2.1 Influence of passivation temperature on black passivation film Temperature is a key factor affecting the progress of chemical reaction, which is very important for obtaining a passivation layer with good appearance and excellent performance [7]. The trivalent chrome black passivation process has a wide operating temperature range. Figure 1 shows the effect of temperature on the appearance of the passivation film. The investigation found that when the temperature is too low, the coating will be slightly brown, and when the temperature is too high, the coating will be colored. Figure 2 is the effect of temperature on the corrosion resistance of the passivation film. Corrosion current and corrosion potential are shown in Table 1. It can be seen from Fig. 2 and Table 1 that the corrosion resistance of the film layer is firstly improved as the passivation temperature is increased, and when the temperature is too high, the corrosion resistance is lowered. Because the film formation speed is too slow when the temperature is too low, the chromium film is too thin under the same conditions at the same time, and the substrate is not completely covered, and the corrosion resistance is poor. As the temperature increases, the rate of formation of the film increases. When the temperature is too high, the formation speed is too fast, resulting in insufficient crystallinity, loose film structure, and poor protection.
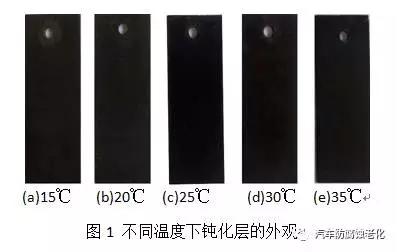
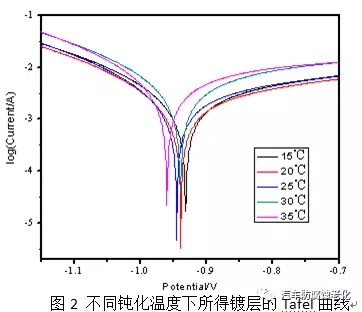
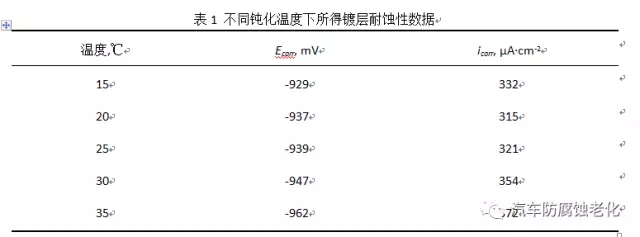
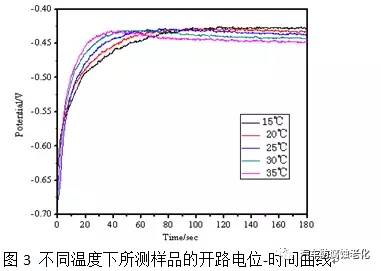
Figure 3 shows the open circuit potential of the zinc-nickel alloy coating in the passivation solution at different temperatures as a function of time. The graph shows that at the beginning of the formation of the chrome film, the higher the temperature, the faster the film formation, and the surface of the coating is almost completely covered after 60 s. When the temperature is too high, the surface potential of the coating reaches a maximum and then slightly decreases, possibly because the excessive passivation temperature causes the film to dissolve. It can also be seen from the final equilibrium potential that when the temperature is low, the film formation is relatively fine, the surface potential of the film layer is positive; the temperature is high, the film formation is relatively fast, the structure is loose, and the film potential is negative.
2.2 Effect of pH value of passivation solution on film properties The principle of zinc-nickel alloy trivalent chromium passivation is that the formation of chromium film is accompanied by the dissolution of zinc layer, and the film-forming process is included at the same time as film formation, eventually forming a Dynamic equilibrium, its formation mechanism is as follows [8]:
a. the oxidant in the solution interacts with H+ and Zn to dissolve the zinc into zinc ions;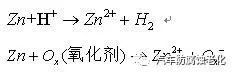
b. The free zinc ions react with the chromium ions in the solution to form insoluble zinc chromium oxide on the surface of the zinc-nickel alloy, and form a black chromium film under the action of the blackening agent, which is the formation of the film.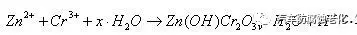
c. The generated zinc-chromium oxide film continues to react with H+ under acidic conditions to form zinc ions and chromium ions, which is called a dissolution process of the film.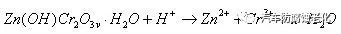
Therefore, the pH of the passivation solution plays a very important role in the film formation process. Figure 4 shows the effect of passivation pH on the appearance of the film. As shown in the figure, in the case where the pH is too low, the film layer is slightly brownish black, and the formed trivalent chromium passivation film is rough, and the hand wipes slightly gray. As the pH increases, the blackness improves, but when the pH is too high, the film begins to bloom. Since the pH is too low, the dissolution of the film layer of the above c process is accelerated, and a porous porous film layer is formed, and the adhesion is lowered. When the pH is too high, it will affect the entire film formation process of the passivation film, resulting in the film layer being too thin.
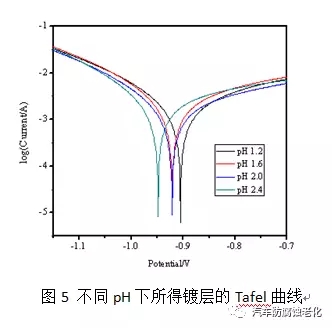
Figure 5 shows the polarization curves of the film obtained in different pH value passivation solutions in NaCl. The corrosion current and corrosion potential are shown in Table 2. It can be seen from Fig. 5 and Table 2 that when the pH of the passivation solution is 1.2, the potential is the most positive. As the pH increases, the corrosion potential gradually shifts negatively. It may be because the lower the pH, the passivation speed is fast, in the same time. The film layer is thick and has good corrosion resistance, but the corrosion current density at pH 1.2 is obviously high. This result may be caused by the loose structure film formed by the too fast film formation speed, so the corrosion rate is accelerated. For a comprehensive investigation, the pH of the passivation solution was chosen to be 1.6 to 2.0.

2.3 Influence of passivation time on film properties In order to obtain a good black film layer, controlling the passivation time is also an important factor. In this experiment, the performance difference of the film obtained by passivation time 20~100s was investigated. Figure 6 shows the appearance of the workpiece obtained at different passivation times. It can be seen from the figure that the blackness of the passivation film is not good for 20s~40s, and the film is black after passivation for more than 60s, but when the passivation time exceeds 80s, the film layer The gloss began to drop and there was a slight ash at the edge of the workpiece.

2.4 Effect of zinc ion on the properties of the film The mechanism of trivalent chromium passivation shows that zinc is dissolved during the passivation process. Therefore, the acceptance of zinc ion by the passivation process was investigated in this experiment. Figure 7 shows the effect of zinc ions on the corrosion resistance of the film. It can be seen from the polarization curve that zinc ions have little effect on the corrosion resistance of the passivation film. When the zinc ion concentration reaches 10g/L, the corrosion potential is negatively shifted by 34mV. It is recommended that the concentration of zinc ions not exceed 10g during the production process. /L.
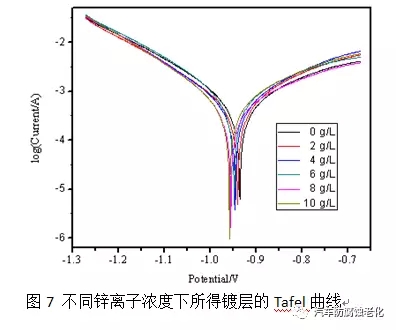
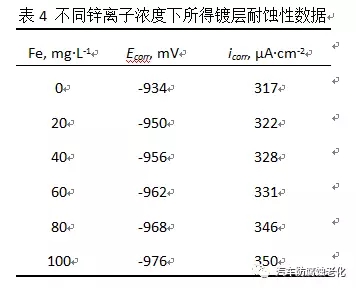
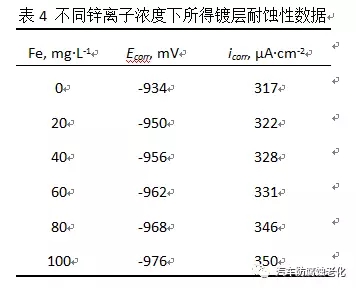
2.5 Effect of iron ions on the properties of the film From the early research, it was found that the influence of iron ions on the corrosion resistance of the film in the trivalent chromium passivation solution is relatively large. Therefore, in the experiment, different known concentrations are added to the passivation solution. Iron ions, the concentration of iron ions that can be withstood by the passivation solution was examined. Figure 8 is a graph showing the effect of iron ions on the corrosion resistance of the film. It can be seen from the figure that when the concentration of iron ions in the passivation solution exceeds 100 mg/L, the corrosion potential is negatively shifted and the corrosion resistance is lowered. The liquid should be treated, otherwise it will affect the quality of the passivation film.
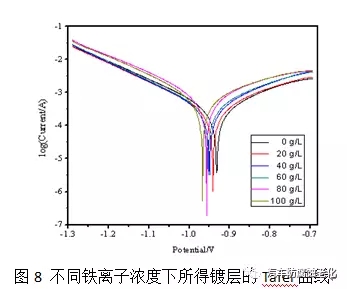
2.6 Neutral salt spray experiment The salt spray test was carried out on the workpiece according to GB/T 6461-2002. Zinc-nickel alloy coatings will gradually appear white corrosives (commonly known as white rust) after salt spray corrosion in neutral salt spray experiments. When the passivation layer is corroded and penetrated, zinc-nickel plating is exposed, and zinc is exposed in a humid environment. Oxidative damage, the process is as follows:
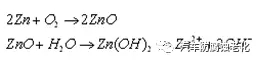
However, because NaCl also produces white crystals, it is easy for people to make mistakes in judgment. This experiment judges the generation of white rust from two aspects:
(1) The observed white spots of corrosion will increase with time. If there is no change, the salt will crystallize. White rust is a corrosion product, which will become larger as the corrosion progresses.
2 Since the corrosion product is alkaline, a drop of phenolphthalein can be dropped on the white spot. If it is changed from colorless to red, it is white rust. If there is no discoloration, it should be crystal of salt.
As can be seen from Fig. 9, the sample showed white rust after a continuous salt spray test for 240 hours, and red rust occurred in 360 hours.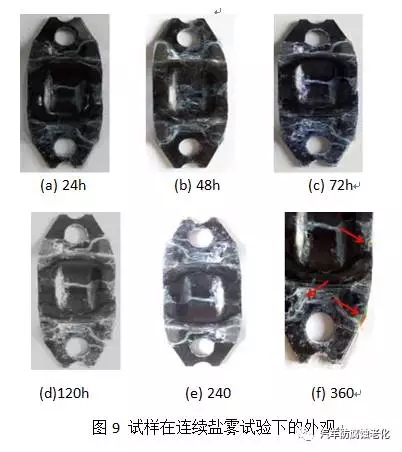
3 Conclusions (1) The optimum process conditions for trivalent chromium black passivation of zinc-nickel alloy are: operating temperature 25 ° C, pH 1.6~2.0, passivation time 60s. The solution should control the zinc ion concentration within 10g/L and the iron ion concentration to be no higher than 100mg/L.
(2) The passivation layer obtained under the optimum process conditions has a black appearance and good corrosion resistance.
A hydraulic quick coupler is a device used to quickly and easily connect and disconnect hydraulic hoses and attachments. It is commonly used in construction, agriculture, and other industries where hydraulic systems are used.
The quick coupler typically consists of two main components: a male coupling and a female coupling. The male coupling is attached to the Hydraulic Hose or attachment, while the female coupling is attached to the hydraulic system.
To connect the hydraulic hose or attachment, the male coupling is inserted into the female coupling and securely locked into place. This can be done by sliding or twisting the couplings together, depending on the specific design.
The quick coupler allows for a fast and efficient connection and disconnection of hydraulic hoses and attachments, saving time and effort. It also provides a secure and leak-free connection, ensuring the hydraulic system operates properly.
There are different types of hydraulic quick couplers available, including flat face couplers, poppet couplers, and ball couplers. Each type has its own advantages and is suitable for different applications.
Overall, a hydraulic quick coupler is an essential tool for anyone working with hydraulic systems, as it provides a convenient and reliable way to connect and disconnect hydraulic hoses and attachments.
Hydraulic Quick Coupler; Quick Coupler; Hydraulic accessory; Hydraulic coupler; Hydraulic spare part
Yantai Dongyue Hydraulic Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.deeleap.com
