Antibacterial technology is increasingly used in the textile industry. According to relevant experts, in the next eight years, the global antibacterial textile market will grow at an annual rate of 10%. Health, natural and environmental protection will become the development trend of textiles in the new century.
1 The main antibacterial mechanism of anti-bacterial textiles
1.1 Release mechanism
The antibacterial finished fabric will automatically release an antibacterial agent at normal temperature and appropriate humidity, which is released in an amount sufficient to kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria, fungi and mold.
1.2 Regeneration mechanism
In the process of washing the antibacterial fabric, the antibacterial agent is regenerated due to the chemical bond breakage of the fiber-antibacterial agent, so that the antibacterial agent content on the surface of the fabric can be maintained at a certain equilibrium state.
1.3 Static inhibition mechanism
The cationic antibacterial agent is bonded to the surface of the fabric by a certain cationic substance and the negatively charged fiber to form a barrier of bacteria, fungi and mold, thereby achieving a static bacteriostatic effect.
2 Application practice of antibacterial finishing technology
According to the understanding of the domestic antibacterial agent market, SCJ-2000, an antibacterial agent produced by Beijing Jieshuang Technology Co., Ltd. with comprehensive performance and excellent indicators, was selected as the raw material of this test.
Antibacterial finishing agent Sq-2000 has the characteristics of broad spectrum, high efficiency, good safety, washing resistance and convenient processing. It is suitable for antibacterial and hygienic finishing of cotton, linen, silk, wool, polyester/cotton, nylon, viscose and other fabrics. The test results of the Southern Science and Technology Testing Center of the textile industry show that SCJ-2000 does not contain any harmful substances such as azo, heavy metals and formaldehyde. The antibacterial group carried by the finishing agent can act on the cell membrane of bacteria and fungi, so that the cell membrane is deficient, the permeability is increased, the cytoplasm is leaked inside the cell, and the synthesis of the bacterial protein is also hindered, resulting in the bacterial core protein body. Depletion, which leads to the death of fungi.
2.1 Test materials and methods
2.1.1 Materials
The raw material is antibacterial finishing agent SCJ-2000, softener; the fabric is 2 pieces of bleached cotton woven fabric, each 4g; the test equipment is lOOmL beaker, glass rod, measuring cylinder, tray balance, constant temperature water bath, small rolling car, pipetting Tube, oven.
2.1.2 Test method
After testing the process conditions of different finishing liquid concentrations and different formulations, the results show that the following processes are most ideal.
(1) Impregnation process
Process: fabric-antibacterial soft finishing (bath ratio 1:10) dehydration and drying. Process: The treatment liquid is immersed at room temperature for 10 min, heated to 50-70 ° C and kept for 30-40 min, dehydrated and dried. Process formula: sCJ - 2000 5% (0.W.f.), softener amount. Chemical operation: first add 30mL of clean water to the beaker, then add 10 times diluted sCJ-20002mL, add softener and water to 4OraL after stirring, and mix well.
(2) padding process
Process: fabric-padded antibacterial solution (rolling rate 70%) drying (80 ~ l10 ° C, the fabric does not contain moisture) a tenter (150 ° C, 30s or 120-130oC, 2-4 mim) . Process formula (take the liquid filling rate of 70% as an example): SCJ-2000 50g / L, the right amount of softener. Chemical operation: first add 30mL of water to the beaker, then add SCJ-20002g, then add appropriate amount of softener, and finally add water to 40mL, stir evenly.
3 Antibacterial finishing results
The antibacterial effect of antibacterial fabric samples on Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Candida albicans, Trichophyton rubrum, Glycyrrhiza glabrata, and Fusarium oxysporum was determined by Quine's method. 1.
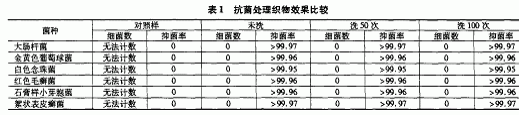
4 Conclusion
The fabric finished by the antibacterial finishing agent SCJ-2000 has strong antibacterial effect. After washing 100 times, it still has high antibacterial effect on bacteria and fungi, and the inhibition rate is over 99.9%, and can inhibit A variety of bacteria and fungi.
references:
[1] Shang Chengjie. New dyeing and finishing auxiliaries manual [M]. Beijing: China Textile Publishing House. 2002, (1O): 241 ~ 248.
Plate rolling is a process of continuous three-point bending of sheet metal using a plate rolling machine. The equipment puts the sheet material between the upper and lower work rolls when rolling. The upper roller is raised and lowered vertically, and the two lower rollers rotate and move horizontally relative to the axis of the upper roller. When the upper roll descends, the plate is plastically deformed and bent between the upper and lower work rolls. The continuous rotation of the bottom roller drives the steel plate to advance and retreat through the friction between the plate and the roller to complete the coiling.
1. Pre-bending. When the plate is rolled, there is a length at both ends of the plate that does not bend because it does not touch the upper roller. It is called the remaining straight edge. In the process, the minimum force arm at which the plate starts to bend is called the theoretical remaining straight edge. The bending form (symmetrical bending, asymmetrical bending) is related.
2. Centering. The purpose of centering is to make the generatrix of the workpiece parallel to the roller axis to prevent skew.
3. Roll round. Rolling is the main process of product forming, which is divided into two types: one-time feed and multiple feeds. Multiple feeds are commonly used for rolling thick plates. The number of feeds depends on the technological constraints (such as the maximum allowable deformation during cold rolling) and equipment constraints (such as non-slip conditions and power conditions). When the rebound of the cold coil is significant, a certain amount of overcoiling must be added.
4. Straightening round. The purpose of rounding is to make the curvature of the entire circle as uniform as possible to ensure product quality. The general rounding process is divided into three steps:
(1) Load: According to experience or calculation, adjust the work roll to the position of the required maximum correction curvature.
(2) Rounding: Roll the roller 1 to 2 turns under the corrected curvature to make the entire curling rate uniform.
(3) Unloading: gradually unload the load, so that the workpiece is rolled several times under the gradually reduced correction load.
Rolling Machine,Three-Roller Bending Machine,Four-Roller Bending Machine,Roll Forming Machine
Rugao Yaou Import & Export Trade Co., Ltd , https://www.ntyaoumachinery.com
