Fiber Optic Adapter (also known as Fiber Optic Flange) is an alignment connecting component in optical fiber transmission. Both ends can be inserted into different types of fiber optic connectors to realize different interfaces such as FC, SC, ST, LC, MTRJ, MPO, E2000, etc. The conversion is widely used in optical fiber distribution frame (ODF), optical fiber communication equipment, instruments, etc., with superior performance, stable and reliable. Some fiber optic adapters in the market are also called fiber optic connectors. Actually, these are two different products.
Depending on the fiber optic connector, the fiber optic adapter can provide a corresponding fiber optic connector transfer member.
Applicable fiber connector models are FC, SC, ST, LC, MTRJ, E2000, etc.
Applicable fiber connectors include PC, UPC, and APC.
SC stands for Standard Connector.
ST stands for StraightTip.
FC stands for FiberConnector.
The front part of the "/" indicates the applicable fiber connector model.
The "SC" connector is a standard square type connector and uses engineering plastics. It has high temperature resistance and is not easily oxidized. The optical interface on the transmission device side is generally an SC connector.
The "LC" joint is similar in shape to the SC joint and somewhat smaller than the SC joint.
The "FC" connector is a metal connector and is generally used on the ODF side. The metal connector can be inserted and removed more often than plastic.
There are many types of connectors, in addition to the three described above, there are MTRJ, ST, MU and so on. The "/" indicates the cross-section process of fiber joints, that is, the grinding method. "PC" is most widely used in telecom operators' equipment, and its connector section is flat. "UPC" has a smaller attenuation than "PC" and is generally used. For equipment with special requirements, some foreign manufacturers use FC/UPC for fiber jump inside the ODF shelf, mainly to improve the ODF equipment's own indicators.
"APC" stands for an oblique 8 degree angle polish. The "APC" model is widely used in broadcast and early CATV. The tail end of the fiber has a tilted end face, which can improve the quality of the TV signal. The main reason is the TV signal. It is analog light modulation. When the joint coupling surface is vertical, the reflected light returns along the original path. Because the uneven refractive index distribution of the fiber will return to the coupling surface again, although the energy is very small, but the analog signal cannot completely eliminate the noise, it is equivalent to superimposing a weak signal with time delay on the original clear signal. It is ghosting on the screen. The tailgap tilt angle allows the reflected light not to return along the original path. Normal digital signals generally do not have this problem.
The fiber optic connector is a device for detachable (active) connection between the optical fiber and the optical fiber. It precisely couples the two ends of the optical fiber so that the optical energy output from the emitting fiber can be coupled to the receiving fiber to the maximum extent. It also minimizes the impact on the system due to its involvement in the optical link, which is a basic requirement for fiber optic connectors. To a certain extent, fiber optic connectors also affect the reliability and performance of optical transmission systems.
Optical fiber connectors can be divided into common single-mode and multi-mode connectors for silicon-based optical fibers according to different transmission media, and other optical fiber connectors such as plastics, which can be classified into FC connectors according to the structure of the connector. , SC, ST, LC, D4, DIN, MU, MT and so on. Among them, ST connectors are usually used for cabling equipment ends, such as optical fiber distribution frames, fiber optic modules, etc.; SC and MT connectors are usually used for network equipment. There are FC, PC (including SPC or UPC) and APC according to the shape of the fiber end face; there are also single-core and multi-core (such as MT-RJ) according to the number of fiber cores. Optical fiber connectors have a wide range of applications. In the actual application process, they are generally differentiated according to the structure of the fiber optic connector. The following are some of the more common fiber optic connectors:
FC type
This connector was first developed by Japan NTT. FC is an abbreviation for FERRULECONNECTOR, indicating that the external reinforcement method is to use metal sleeves and the fastening method is a turnbuckle. The earliest, FC-type connector used the butt-end of ceramic pins. Such a connector has a simple structure, is easy to operate, and is easy to manufacture. However, the fiber end face is more sensitive to micro dust, and Fresnel reflection is more likely to occur. Therefore, it is difficult to improve the return loss performance. Later, this type of connector was modified to use a pin (PC) with a spherical butt-end face, and the external structure did not change, resulting in a significant increase in insertion loss and return loss performance.
Type SC
This is a fiber optic connector developed by NTT Japan. The housing is rectangular, and the pin and coupling sleeve used are of the same size as the FC type. The end face of the pin is mostly PC or APC-type grinding; the fastening method is the use of plug-and-pin latch type, no need to rotate. These connectors are inexpensive, easy to insert and pull out, have a small fluctuation in insertion loss, high compressive strength, and high installation density.
The ST and SC interfaces are two types of fiber optic connectors. For 10BASE-F connections, the connectors are usually ST type. For 100BASE-FX, the connectors are mostly SC type. The core of the ST connector is exposed, and the SC connector core is inside the connector.
Double cone type
The most representative of these types of fiber optic connectors is developed by Bell Labs, USA. It consists of two precision-molded tips with a truncated-cone-shaped cylinder plug and an internal double-tapered plastic sleeve. The coupling components of the cartridge are composed.
DIN47256 type
This is a connector developed by Germany. The pins and coupling sleeves used in this type of connector have the same structural dimensions as the FC type. The end face treatment uses PC grinding. Compared with the FC type connector, the structure thereof is more complicated, and the inner metal structure has a spring for controlling the pressure, so as to avoid damage to the end surface due to excessive plug pressure. In addition, the mechanical precision of this connector is high, so the insertion loss value is small.
MT-RJ type
MT-RJ started from NTT developed MT connector with the same latch mechanism as RJ-45 type LAN electrical connector. It is aligned with the optical fiber through guide pins installed on both sides of the small sleeve for easy communication with the optical transceiver. Connected to the machine, the connector end face fiber is a twin-core (interval 0.75mm) array design and is the next-generation high-density fiber optic connector for data transmission.
Type LC
The LC connector was developed by the famous Bell Institute and is made using the convenient mechanism of the modular jack (RJ) latch mechanism. The size of the pins and sleeves used is half of the size used for ordinary SC, FC, etc., which is 1.25 MM. This can increase the density of fiber connectors in the fiber distribution frame. At present, in the aspect of single-mode SFF, the connector of LC type has actually occupied the dominant position, and the application in multimode has also grown rapidly.
MU type
The MU (MINIATURE UNIT COUPLING) connector is the world's smallest single-fiber connector developed by NTT based on the SC type connector currently used most. The connector features a 1.25mm diameter sleeve and self-retaining mechanism, which has the advantage of enabling high-density mounting. Using MU's L.25MM diameter bushings, NTT has developed MU connector series. They have a socket type connector (MU-A series) for optical cable connection; a backplane connector (MU-B series) with a self-retaining mechanism and a simplified socket for connecting an LD/PD module and a plug (MU-SR series) Wait. With the rapid development of larger bandwidth and larger capacity of optical fiber networks and the wide application of DWDM technology, the demand for MU-type connectors will also increase rapidly.
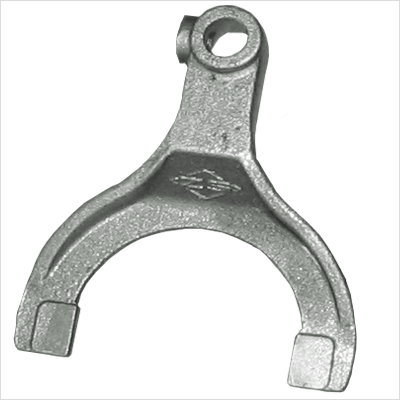
Shift Fork
Shift
fork normally applied in the transmissions, its function
is help to slide gears into or out of engagement with other gears in order to
change from one gear ratio to another in a manual transmission.
QFAP supply various kinds of shift forks to all over the world, main of our customers are
digger/excavators manufacturers, lawn mower manufacturers, truck transmission
factories and construction machinery companies.
Materials:
carbon steel castings, stainless steel castings, alloys steel castings, aluminum
die castings, forging steel castings, etc.
Surface treatment: painting, zinc plating, passivation,
nickel plating, anodizing, polishing, etc.
Heat treatment: according to customer`s
requirement.
QFAP have specialized in producing high
precision Agriculture Parts more
than 10years, Because of the long term cooperation, we could supply our
customers not only the products but also our recommendation on the designs to
saving costs.
Shift Fork,Shift Fork Gear,Transmission Shift Fork,Reverse Shift Fork
SHAOXING QIFENG AUTO PARTS CO., LTD. , https://www.sxqfap.com

