This season's summary: The temperature in most of the country's agricultural areas is close to normal or slightly higher. The precipitation in the western part of the northwest, most of North China, Huanghuai, Jianghuai, Jianghan, and the southwestern part of the southwestern region is less, and the rest of the agricultural areas are biased. many. The water-heat matching during spring sowing in Northeast China is better, which is conducive to spring planting and crop seedling growth. In the northern winter wheat area, the temperature in early spring is low, and the development period of winter wheat is delayed. However, from late March to May, the light and heat are sufficient, the precipitation is timely, and the soil moisture is suitable, which is conducive to the growth and yield formation of winter wheat. Most of the southern part of the country in the middle and early March, low temperature, rainy weather, has a certain impact on crop growth and spring sowing; from late March to May, hydrothermal conditions are basically suitable, generally conducive to winter wheat, rapeseed yield formation and mature harvesting Early rice, corn and other crops grow and develop; however, some areas have staged overcast rain and short-term heavy precipitation, which has certain impact on agricultural production. The spring drought in southern Sichuan and northern Yunnan continued, and the yield of summer crops and the growth of spring-sown crops were greatly affected. At the end of May, there was strong precipitation and the drought was significantly eased.
I. Weather and climate characteristics
In spring (March-May 2012), temperatures in most agricultural areas across the country are close to normal or slightly higher (Figure 1). Precipitation in the western part of the Northwest, North China, Huanghuai, Jianghuai, Jianghan, and the southwestern part of the southwest is less, and most of the remaining agricultural areas have more precipitation (Figure 2). The precipitation days in the south of Jianghuai, southern Jianghan, Jiangnan, southern China and the southwestern part of the country are more than 40 days (Fig. 3). The sunshine conditions are poor, and the daily average is less than 5 hours. Most of the northern agricultural areas have sufficient sunshine (Figure 4). 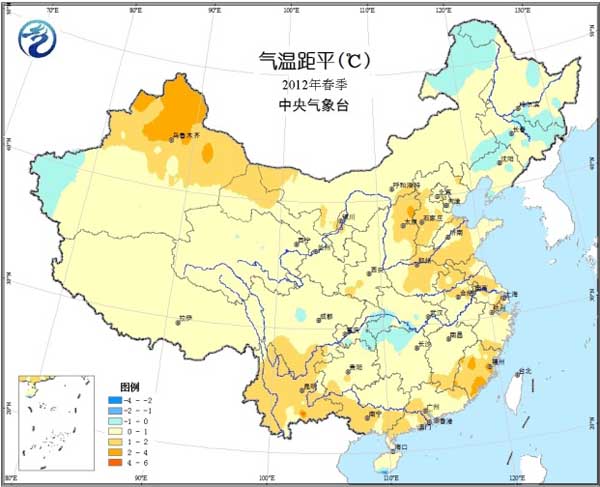
Figure 1 Average spring temperature anomalies in 2012 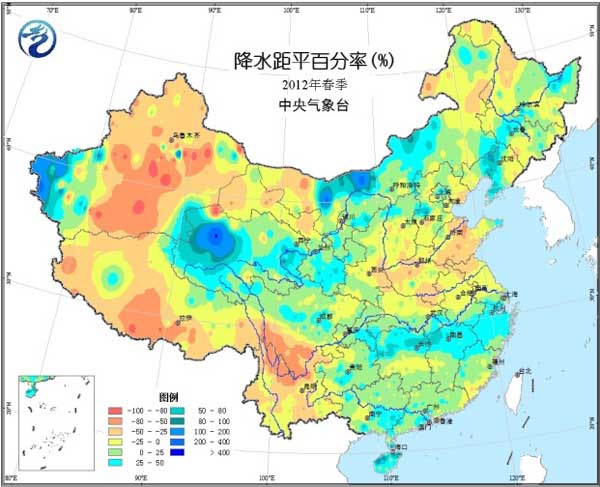
Figure 2 Spring precipitation anomalies in 2012 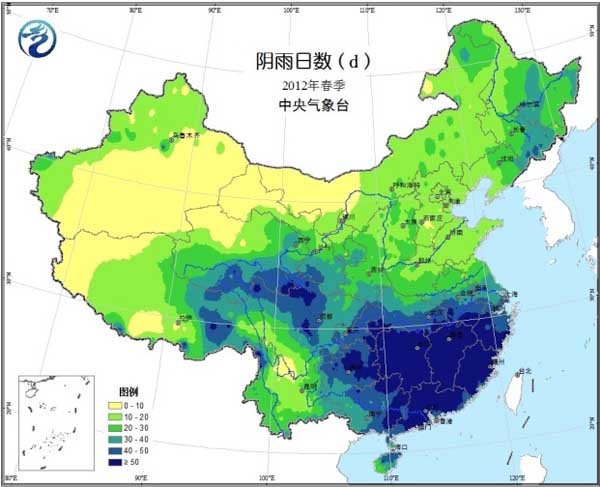
Figure 3 Spring precipitation days in 2012 
Figure 4 Spring sunshine hours in 2012
Second, regional agricultural meteorological conditions analysis
Northeast: In most areas, there was a significant snowfall in March. The maximum snow depth in eastern Inner Mongolia, northern Heilongjiang, central and eastern Jilin, and most parts of Liaoning is more than 5 cm, which is conducive to soil growth and conservation, but low temperature is not conducive to soil thawing and facilities. Agricultural and livestock production. The temperature began to rise sharply in the middle of April. The precipitation in the western region is 25-50 mm, and the east and the south are 50-100 mm, which is close to the same period of the year or slightly more. Among them, on May 12-14, there are 10~ in the western part of the northeast. 25mm precipitation, the sustained drought in the previous period was alleviated, the soil moisture in most agricultural areas was suitable, the hydrothermal conditions were well matched, the spring sowing progressed smoothly, and the crop seedlings grew well.
Northwest, North China, Huanghuai: The temperature in the upper part of March was significantly lower in the middle of March, and the development period of winter wheat was delayed. The heat condition in the late March began to improve, which was conducive to the growth and yield formation of winter wheat. In the eastern part of the northwestern region, north China, and Huanghuai, there were five obvious precipitation processes in the first three months, and the cumulative precipitation reached 30-80 mm. Among them, large-scale flooding occurred on April 23-25, with precipitation of 10-50 mm. The precipitation is just in the critical period of water requirement for winter wheat jointing and booting, which is very beneficial to increase the soil moisture in the wheat area and promote the growth and development of winter wheat. Good soil moisture is also beneficial to the sowing and emergence of spring-sown crops. In May, Shanxi, Hebei and Henan provinces had less temperature and rain, soil moisture decreased rapidly, and some farmland experienced drought. At the end of the month, most of the depleted areas showed 10 to 30 millimeters of precipitation, which effectively supplemented the soil moisture and eased the previous drought.
Jianghuai and Jianghan: Most of the areas in the middle and early March continued to have low temperature and rainy weather. The development period of winter wheat and rapeseed was generally postponed. Some farmland soils continued to be too wet, causing waterlogging, and the long-term deviation and the number of branches of live and late rapeseed were small. After the end of March, the weather in most areas has gradually improved, which is conducive to the growth and maturity of summer grain and oil crops, as well as the sowing and emergence of crops such as cotton, spring corn and rice. However, short-term heavy precipitation or staged rainy weather occurred in parts of Hubei and southern Anhui in May, which had certain effects on the ripening and drying of rapeseed and winter wheat.
Jiangnan and South China: Most of the areas in the middle and early March were mainly low-temperature, rainy and rainy weather, and the dryland crops grew slowly. The early rice planting in the western and northern parts of South China was slow, and the seedlings were weak. The light and heat conditions in the late March improved significantly, which was conducive to the growth of seedlings and the transformation of seedlings in early rice in South China. From April to May, the temperature in most areas is high, and the sunshine is normal. The light and temperature conditions are conducive to the flowering and pod formation of rapeseed, the early rice transplanting and greening and tillering, and the growth of cotton seedlings; but the precipitation in the north of the Yangtze River and the central part of South China is not strong. It is conducive to the ripening and drying of rapeseed, the growth of early rice and the control of sun-dried fields. The growth and development of flue-cured tobacco, vegetables and tropical fruits are also affected. At the same time, the rainy weather causes serious occurrence of pests such as rice planthoppers and rice blast; in addition, heavy precipitation The flooding occurred in some areas, the rape was flooded, and the rice fields were washed away.
Southwest: The light and temperature conditions in most of the Sichuan Basin are generally good, and the soil moisture is suitable, which is conducive to the formation of winter wheat and rapeseed and the timely harvesting of the sun. It is also beneficial to the growth of corn and the tillering of rice in a season. The weather in most parts of Guizhou in mid-March and May was not conducive to crop growth and development, and the progress of summer harvest was delayed. After the spring in southern Sichuan and northern Yunnan, the temperature is still high, and there is no effective precipitation. The drought continues to develop. The summer harvested grain and oil crops without irrigation conditions suffer from severe drought, and the growth of spring-sown crops is greatly affected. At the end of May, most of the dry areas appeared 30. ~ 50 mm precipitation, the drought is significantly eased.
Third, major agricultural meteorological disasters
Drought: The drought in southern Sichuan and northern Yunnan continued to develop, the formation of winter wheat and rapeseed was affected, potato and spring maize were difficult to plant, flue-cured tobacco and one-season rice could not be transplanted in time. In some areas, drinking water was difficult for people and animals, and the obvious precipitation process at the end of May eased the drought. . Most of North China and Huanghuai have higher temperatures in May, with less than 50% precipitation. Some areas in southwestern Shanxi and northwestern Henan have mild drought conditions, which are unfavorable for winter wheat grain filling and spring planting seedling growth. Shanxi at the end of May The Ministry of Agriculture and the northwestern part of Henan Province experienced a moderate easing of 10-30 mm precipitation.
Heavy rains and floods: Jiangxi, Hunan, Guangdong, Fujian, Guizhou and other places have strong precipitation weather from April to May. The number of rainstorm days is 3 to 9 days, and some areas are 9 to 12 days, causing floods in some areas. Farmland and fish ponds are flooded, and the growth of rapeseed, pod, early rice and flue-cured tobacco is also adversely affected. In addition, the snow in the Ili Valley in Xinjiang is thicker in winter, and the temperature rises rapidly after entering the spring. In the middle of March, snowmelt floods occur, causing some farmland to be flooded, vegetable greenhouses and livestock enclosures to collapse, and young animals to die.
Even the rain and waterlogging: the southeastern part of the Yangtze River, the Jianghan, the Jiangnan, the South China, and the southwestern part of the country experienced long periods of rainy and sloppy weather in mid-March, resulting in some farmland soils continuing to be too wet, with obvious waterlogging, rotten roots and dead seedlings.
Gale: In the northwest, Inner Mongolia, North China, Huanghuai, Hubei, Yunnan and other places, windy weather occurred in March, and dust appeared in some areas, causing winter wheat to fall and rubber, banana and other crops to be damaged. In addition, in some parts of Xinjiang, winds and dusty weather occurred on April 21-23 and May 9, causing damage to vegetable greenhouses, collapse of livestock enclosures, and destruction of local cotton mulch.
Hail: Shandong Jinan and Weifang, Jilin Baicheng, Gansu Dingxi City, Tianshui City, Pingliang City and Wuwei City, etc., have hail disasters in May, causing mechanical damage to winter wheat, spring wheat and spring corn, and some facilities agriculture affected.
Snow disaster: snowstorms occurred in Yushu, Qinghai and Sichuan Shiqu in early March. Due to the large amount of snowfall, the snow is deep, and the snowfall process lasts for a long time, and the animal husbandry is affected.
Pests and diseases: Most of the northern winter wheat area is high in the period from late April to May, and there are 3 to 10 days of hot weather with a maximum temperature of ≥30 °C, causing wheat aphids in Anhui, Jiangsu, Henan, Shandong, Hebei, Gansu and other places. The area of ​​occurrence has expanded rapidly, the density of insect population has risen sharply, and high-density fields have appeared locally, which is unfavorable for the production of winter wheat. In the southern rice region, there are many strong precipitation events in May, Yunnan, Guizhou, Guangxi, Guangdong, Hunan, Jiangxi and other provinces. Rice blast and other occurrences are heavier.
4. Prospects and recommendations for agricultural meteorological conditions
It is estimated that in summer (June-August), the temperature in most parts of the country is high, and the number of high-temperature days in Jiangnan, eastern Sichuan, Chongqing and other places is high. It is unfavorable for early rice, first-season rice heading, flowering, and late rice seedling growth and tillering. There may be staged low temperatures in the early summer in the south, and crop growth such as rice and corn may be slightly affected. The main rainy areas in summer will be located in the southern part of North China, Huanghuai, Jianghuai and other places. Floods may occur in the Huanghuai area, which is unfavorable for crop growth and yield formation. In northern Xinjiang, central Inner Mongolia, Jiangnan and other places, precipitation is less, and some areas may In the event of drought, both agricultural and livestock production will be affected. In addition, it is expected that the number of tropical cyclones landing in China will be more than normal in the summer, and the precipitation in the southeastern coastal areas will be more than normal. The floods and gale disasters caused by typhoons are not conducive to crop growth and aquaculture. Suggest:
1. The northern spring sowing area should strengthen field management, timely cultivating and fertilizing, and timely irrigation in the dry areas to promote the steady growth of spring-sown crops and strive to form a high-yield group.
2. In the northern winter wheat area, we should harvest mature winter wheat in time to achieve high yield and harvest; in the end of summer harvest, we should plant summer corn, summer soybean and other crops to ensure that Miao Qi and Miao Zhuang are strong; Avoid delays in farming time.
3, Jiangnan, South China early rice production area should do early rice management, prevent the impact of high temperature on early rice, to ensure high yield and stability; early rice harvest after harvesting to ensure the timely transplanting of rice, and depending on the seedlings, growth, moderate Fertilize to promote tiller growth.
4. After the summer, strong precipitation and strong convective weather will increase everywhere. All localities should strengthen flood control work, keep the ditch clear, and reduce the harm of heavy rain and flood disasters to agricultural production.
5. All localities should strengthen the monitoring and prevention of pests and diseases.
solar street light
solar flood light
highbay light
grow light
Smd Flood Light,Explosion-Proof Led Flood Light,Smd Led Flood Light,Aluminum Led Flood Light
zhongshanshi huadengxing lighting co., ltd , https://www.ledhdx.com
