 |
At present, most photovoltaic devices (ie, solar cells) are absorbed by visible light, and occupying 52% of the near-infrared light in the sunlight has not been efficiently utilized. Because of this, enhancing the absorption and utilization of sunlight in the near-infrared region has become a key scientific issue, and specific requirements have been put forward for the design of device types and mechanisms.
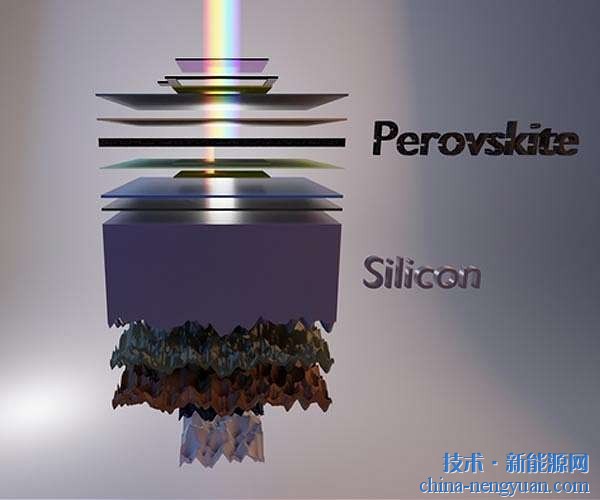
In response to this key issue, recently Professor Xiong Yujie of the University of Science and Technology of China, based on the highest content and most widely used semiconductor silicon material on the earth, adopted the plasmonic hot electron injection mechanism of metal nanostructures to design a kind of near infrared Photovoltaic devices with photoelectric conversion and mechanical flexibility. The study was published on the German Applied Chemistry on March 1 and was selected as a very important paper in the journal. The first author of the dissertation was Dr. Liu Dong and Yang Dong.
Researchers have introduced silver nanosheet structures with near-infrared plasmon absorption bands into inorganic-organic heterojunctions and Schottky-types based on hot carrier injection effects at the semiconductor-metal interface previously studied by the research group. In photovoltaic devices, the photoelectric conversion performance in the near-infrared region has been improved. Under near-infrared light, hot electrons generated by the plasmon effect can be directly injected into the conduction band of the silicon semiconductor, and the photoelectric conversion quantum efficiency in this band is increased by 59%.
On the other hand, traditional inorganic optoelectronic devices must be processed into rigid plate-like objects, limiting their many everyday uses. In contrast, flexible devices are lightweight and can be folded, curled, and glued to curved surfaces. Therefore, while everyone is dedicated to improving the photoelectric conversion efficiency of photovoltaic devices, they are constantly striving to improve their mechanical flexibility so that they can be quickly and easily applied to daily life and high-end applications. In response to the problem of mechanical flexibility, Xiong Yujie's task force thinned and etched nano-wires on commercial silicon wafers, and then combined the plasmonic hot electron injection effect of silver nano-sheets to create a near-infrared solar cell with mechanical flexibility.
The work achieved an effective combination of “bottom-up†and “top-down†nanotechnology, which provided a precise manufacturing foundation for the design of composite structure interfaces for broad-spectrum light absorption, and developed a simple and effective method. Near-infrared flexible solar cell manufacturing method. The study also proposed a new interface engineering idea, promoted the application of hot electron injection mechanism, and will expand people's ability to control the "microscopic engine" of electronic motion in energy conversion.
The research work was supported by projects supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Youth 1000 Program, the 100-person Plan of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Advanced User Fund of Hefei University Science Center, the Special Research Fund for Doctoral Programs of Higher Education Institutions, and the Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities.
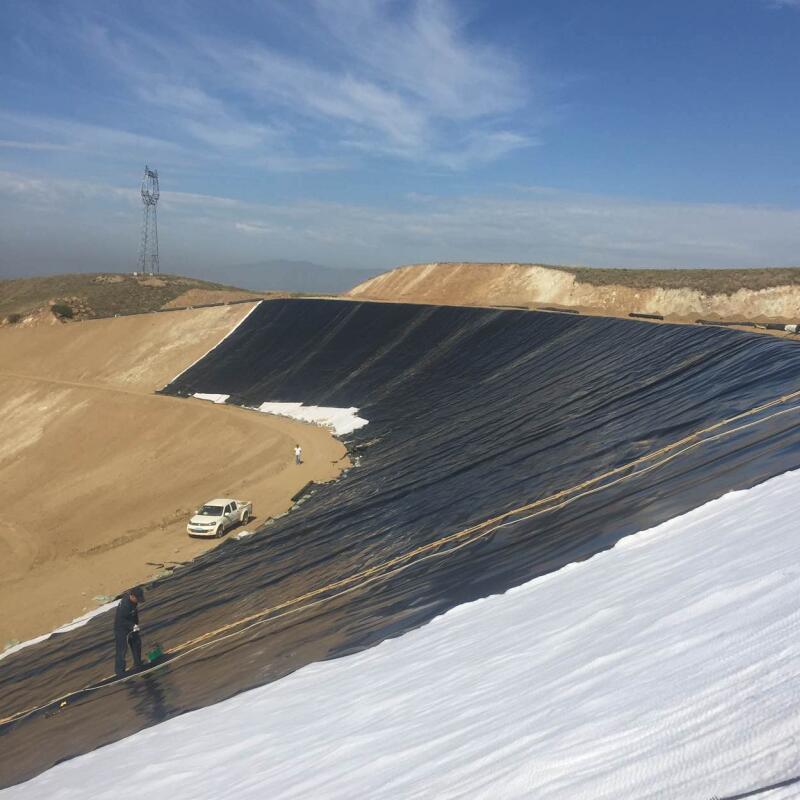
PET short fiber needle punched nonwoven Geotextile Made from polyester(PET)short fiber by nonwoven needle punched manufacturing process, it has isolation, filteation,drainage, reinforcement, protection and maintenance etc. function.

Application Areas
Used in motorways, sport facilities, tunnels and underground facilities, art buildings, underground, agricultural areas, garden terraces, airports, mining fields, railways, solid waste storage areas, irrigation channels and reservoirs, shore protection and isolationareas; as a reinforcementagainst cracks between insulation layers; as a separator between waterproofing and thermal insulation layers; to protect insulation; to drain excess water; to prevent drainage pipes from plugging by wrapping them around; to avoid sinking and in many other applications.



Needle Punched Nonwoven Short Filament Geotextile Technical Parameter
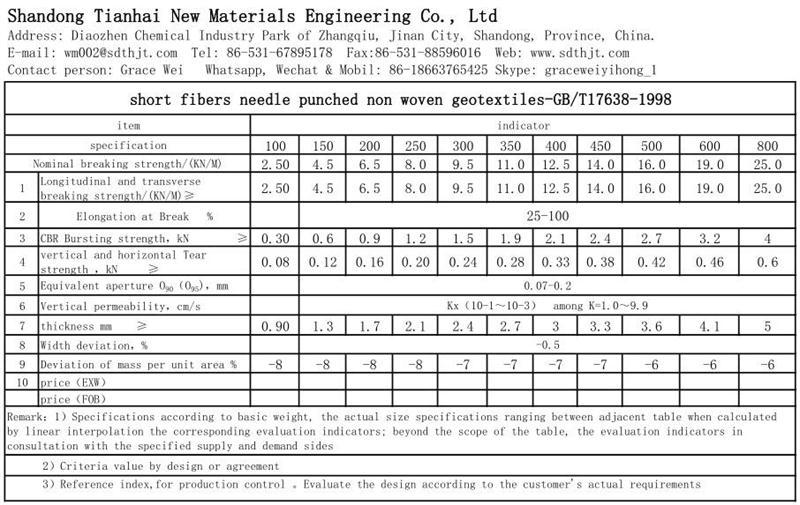
Unit Weight of Geotextile
100g/m2, 150g/m2, 200g/m2, 250g/m2, 300g/m2, 350g/m2, 400g/m2, 450g/m2, 500g/m2, 600g/m2, 800g/m2 or customerized
Contact:

Pet Short Fiber Nonwoven Geotextile
Pet Short Fiber Nonwoven Geotextile,Short Fiber Nonwoven Geotextile Fabric,Pet Composite Geotextile,Short Fiber Geotextile
Shandong Tianhai New Materials Engineering Co., Ltd , https://www.chinatinhy.com
