Lithium-magnesium double-salt electrolyte activated, large-capacity organic magnesium battery based on nano-structure roseotonic acid salt
The application of large-scale energy storage devices represented by smart grids places higher requirements on the cycle life, power density, cost, and safety of energy storage cells. The room-temperature secondary magnesium-based battery is a type of electrochemical energy storage system using metal magnesium as the negative electrode. It has a rich negative-electrode crust, low cost (the price of metal magnesium is less than 5% of the price of metal lithium), and has a large volumetric capacity (3833 mAh). /cm3), No advantage of dendrite formation during electrochemical cycling, and the theoretical reduction potential of magnesium ions is only about 0.6V higher than that of lithium ions. As long as a suitable positive electrode structural framework is adopted, magnesium-based batteries can still maintain lithium. Ion batteries have comparable energy density. Furthermore, the stable reversible deposition/exfoliation of magnesium ions helps to suppress the volume expansion at the negative electrode end, reduces electrolyte consumption, and significantly improves the cycle life and power density of magnesium-based batteries. Therefore, magnesium-based batteries can meet the requirements of the next-generation energy storage system without sacrificing energy density.
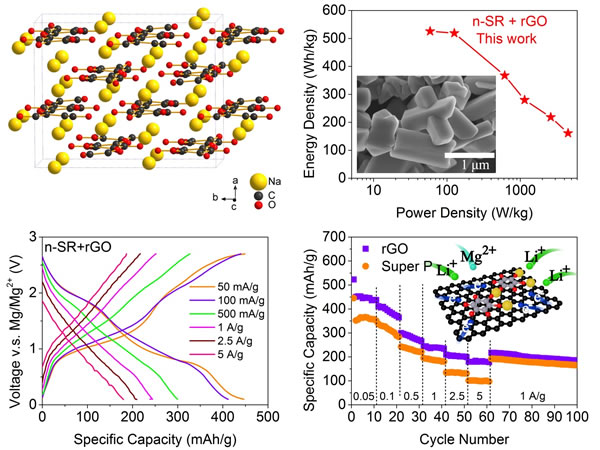
However, the disadvantages of slow migration of magnesium ions within the lattice and low theoretical capacity of inorganic frameworks still limit the widespread use of magnesium batteries. Lithium-magnesium double-salt electrolyte system can achieve positive polar dynamics activation by predominantly lithium ions (instead of magnesium ions) embedded in the positive lattice without sacrificing the stability of the magnesium metal negative-electrode cycle and avoiding magnesium ion dynamics. The disadvantage of poor performance greatly expands the choice of magnesium battery cathode materials. Recently, the team led by Li Chilin, a researcher at the Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, proposed a double-salt electrolyte-activated multi-electron-reactive organomagnesium battery with a green, renewable rosellite salt (such as Na2C6O6). Relevant results were published in the American Chemical Society's publication ACS Nano (DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.7b09177).
Nanostructured organic systems with high density of carbonyl groups (C=O) as redox sites can achieve up to 350-400 mAh/g of reversible capacity (three-electron transfer), which can be further reduced by reducing graphene oxide (RGO) wiring High-rate electrochemical performance is achieved at 2.5 A/g (5 C) and 5 A/g (10 C) current densities of 200 and 175 mAh/g, respectively, and high rate performance also benefits from Under high current and long cycle conditions, the magnesium negative electrode still has no dendrite formation. This excellent performance benefits from the high intrinsic diffusion coefficient of lithium in Na2C6O6 (10-12-10-11 cm2/s) and a tantalum capacity contribution of greater than 60%, a stronger non-lithium pinning effect (via Na-OC and Mg- (Occurrence of OC) can suppress peeling of the C6O6 layer in the crystal grain and realize a charge and discharge cycle of at least 600 times. The positive electrode active material of this organic magnesium battery can have an energy density of more than 500 Wh/kg, and a power density exceeding 4000 W/kg can be tolerated. This performance exceeds the level of a high-potential embedded cathode material based on an inorganic structure.
The team has long been dedicated to the study of kinetics improvement strategies for magnesium-based batteries. In the early days, an anion-embedded activated, exposed magnesium fluorinated graphene battery (Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 6519–6526) has been developed. A dual-salt magnesium-based battery based on a large-capacity polysulfide conversion reaction (AdvFunct Mater. 2015, 25, 7300-7308) was proposed to implement a large-rate, long-cycle Mg-S battery (Adv Mater. 2018, 30, 1704166).
The research work has received funding and support from the National Key R&D Program, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Chinese Academy of Sciences 100-person Plan and the Shanghai Qianren Project.
Kitchen sink
The main purpose of the kitchen sink is to wash food, wash dishes, etc. According to the style, it can be divided into Apron Sink, workstation, Topmount Sink, Undermount Sink and so on. The sink is mainly made of 304 stainless steel, which is resistant to corrosion, oxidation, good toughness and durability.
Over 10 years global trade of stainless steel handmade kitchen sinks experience.
High quality 304 or 201 stainless steel material, apply advanced nano technology.
Customized different sizes and colours to satisfy different demands.
Kitchen Sink,Farmhouse Sink,Copper Sink,Stainless Steel Sink
Jiangmen MEIAO Kitchen And Bathroom Co., Ltd. , https://www.meiaosink.com
